Semantic Image Analogy with a Conditional Single-Image GAN
| Paper | Video | Code |
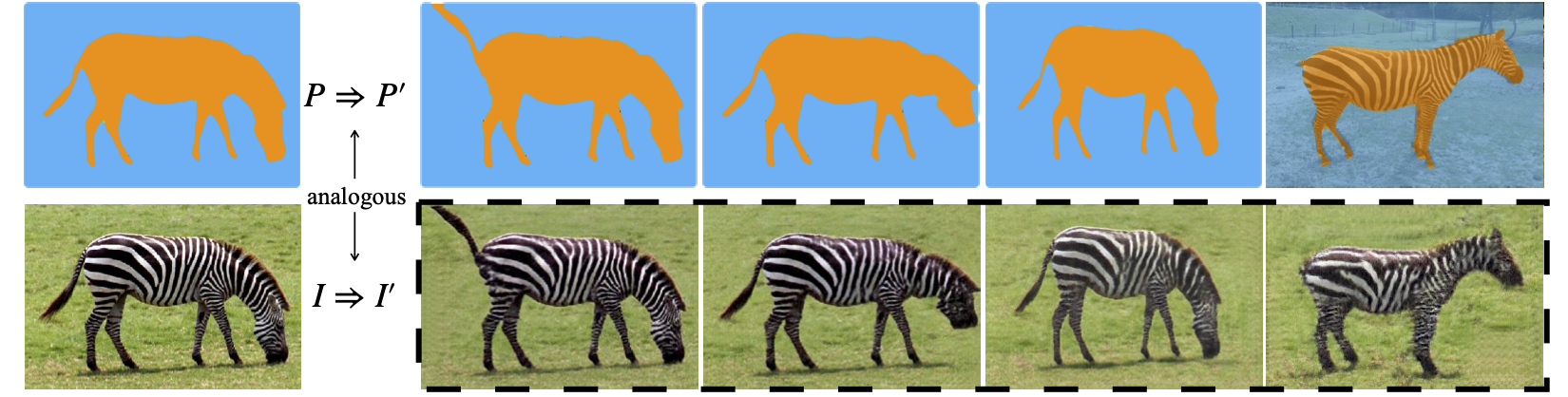
Semantic Image Analogy: given a source image $I$ and its segmentation map $P$, along with another target segmentation map $P’$, synthesizing a new image $I’$ that matches the appearance of the source image as well as the semantic layout of the target segmentation. The transformations from $P$ to $P’$ and from $I$ to $I’$ are semantically ``analogous’’.
Abstract
Recent image-specific Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) provide a way to learn generative models from a single image instead of a large dataset. However, the semantic meaning of patches inside a single image is less explored. In this work, we first define the task of Semantic Image Analogy: given a source image and its segmentation map, along with another target segmentation map, synthesizing a new image that matches the appearance of the source image as well as the semantic layout of the target segmentation. To accomplish this task, we propose a novel method to model the patch-level correspondence between semantic layout and appearance of a single image by training a single-image GAN that takes semantic labels as conditional input. Once trained, a controllable redistribution of patches from the training image can be obtained by providing the expected semantic layout as spatial guidance. The proposed method contains three essential parts: 1) a self-supervised training framework, with a progressive data augmentation strategy and an alternating optimization procedure; 2) a semantic feature translation module that predicts transformation parameters in the image domain from the segmentation domain; and 3) a semantics-aware patch-wise loss that explicitly measures the similarity of two images in terms of patch distribution. Compared with existing solutions, our method generates much more realistic results given arbitrary semantic labels as conditional input.
Framework
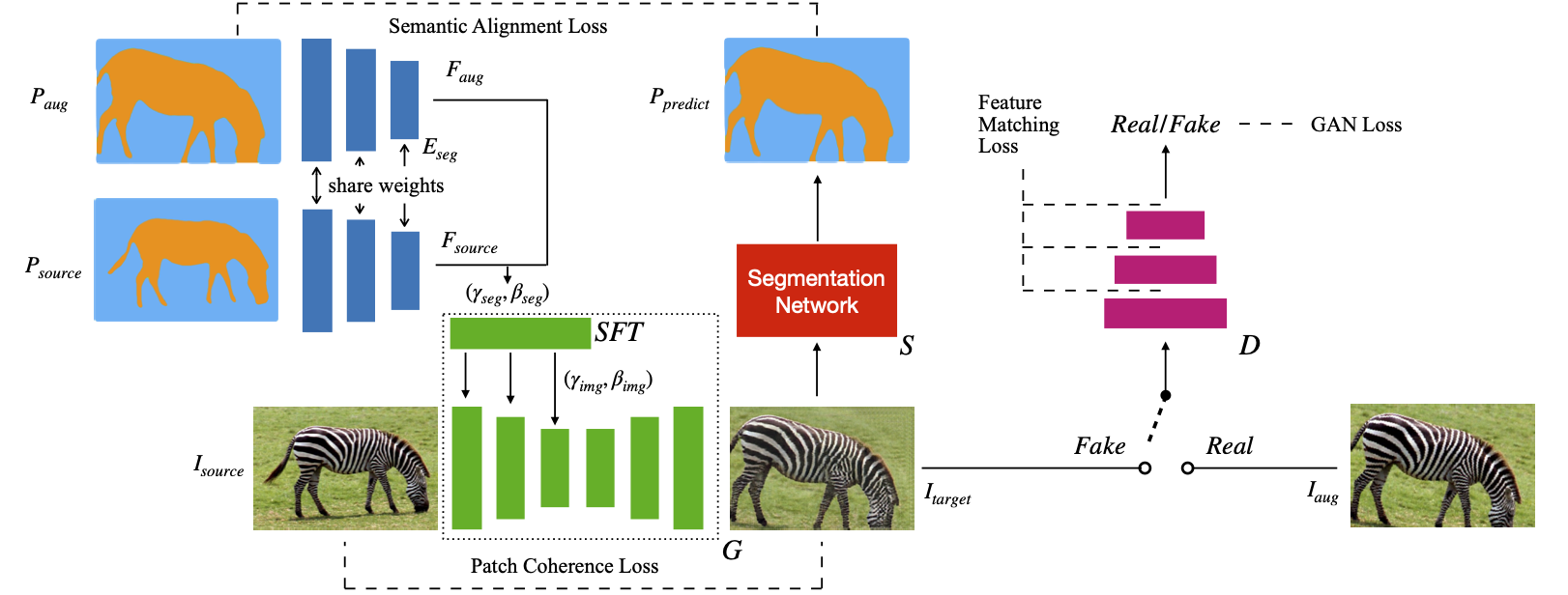
The proposed self-supervised training framework for our conditional GAN. At first, augmentation operations are applied on the source image $I_{source}$ and the source segmentation map $P_{source}$ to obtain $I_{aug}$ and $P_{aug}$ as psuedo lables. Then, the encoder $E_{seg}$ extracts features $F_{source}$ and $F_{aug}$ from $P_{source}$ and $P_{aug}$. The Semantic Feature Translation (SFT) module predicts transformation parameters $(\gamma_{img}, \beta_{img})$ from $F_{source}$ and $F_{aug}$. Finally, the generator $G$ maps $I_{source}$ to the fake image $I_{target}$ under the guidance of $(\gamma_{img}, \beta_{img})$. At the same time, the discriminator $D$ tries to distinguish $I_{aug}$ and $I_{target}$. The auxiliary classifier $S$ predicts the semantic segmentation label $P_{predict}$ of $I_{target}$. The Semantic Alignment Loss between $P_{aug}$ and $P_{predict}$ and the Patch Cohernece Loss between $I_{source}$ and $I_{target}$ are calculated for self-supervision.
Results
Semantic Manipulation
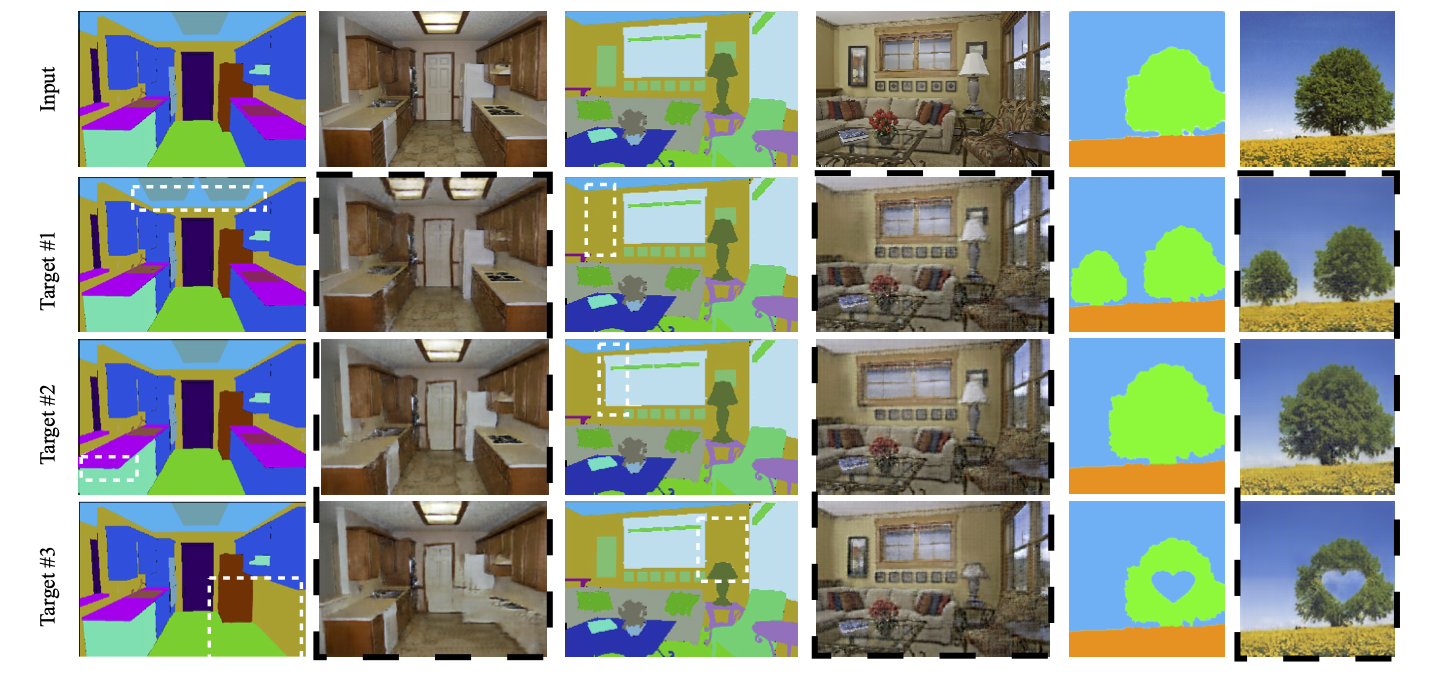
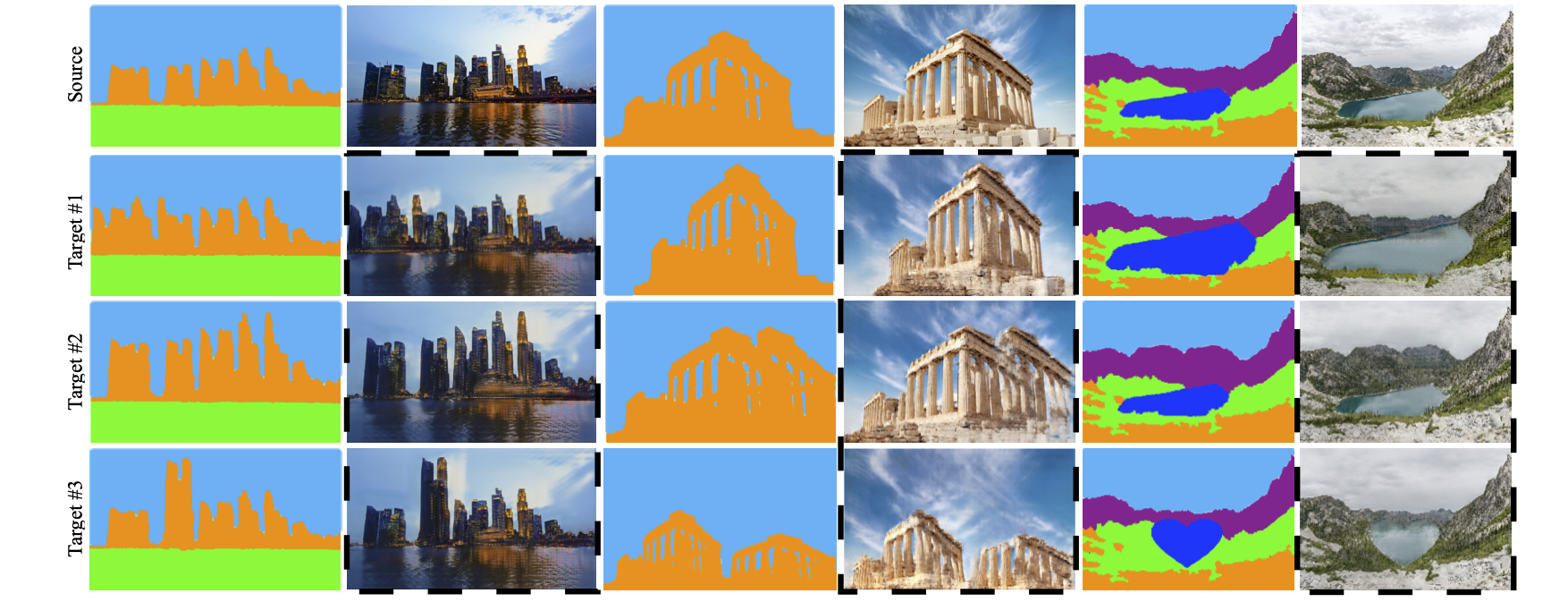


Object Removal
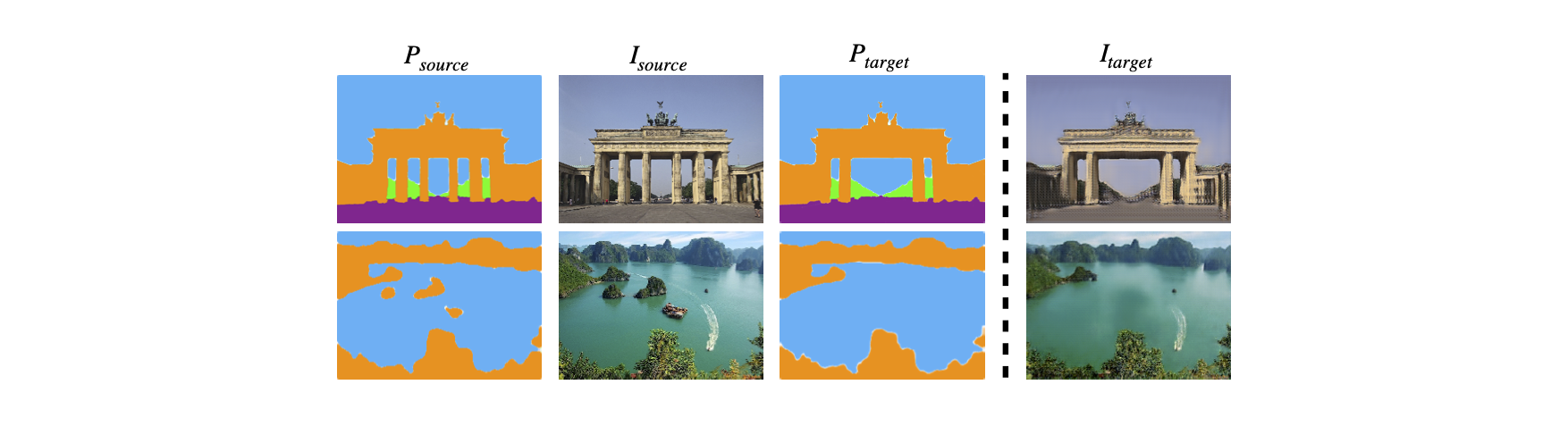
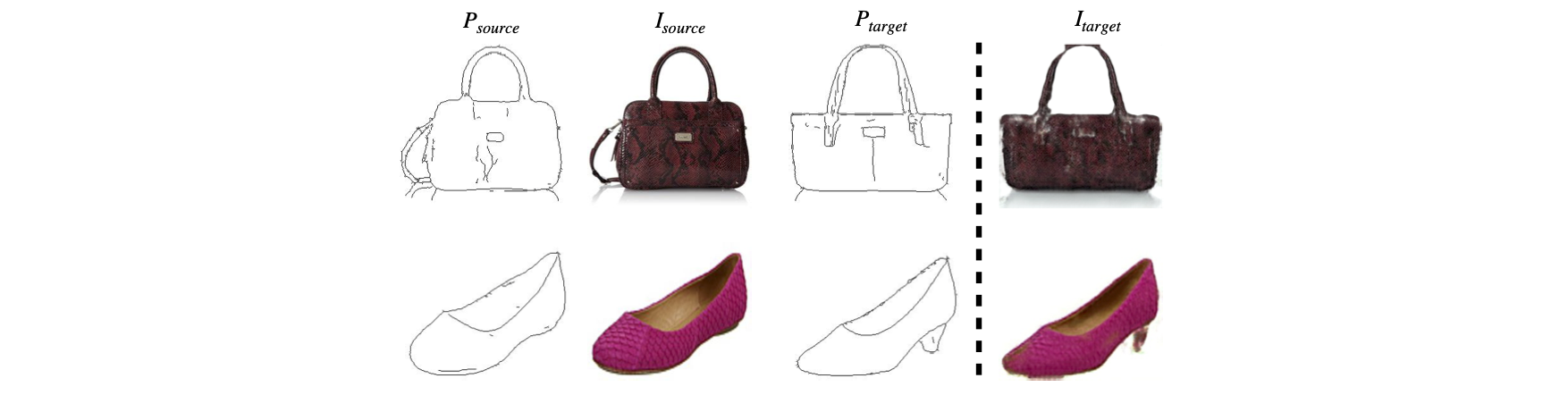
Sketch-to-Image Synthesis

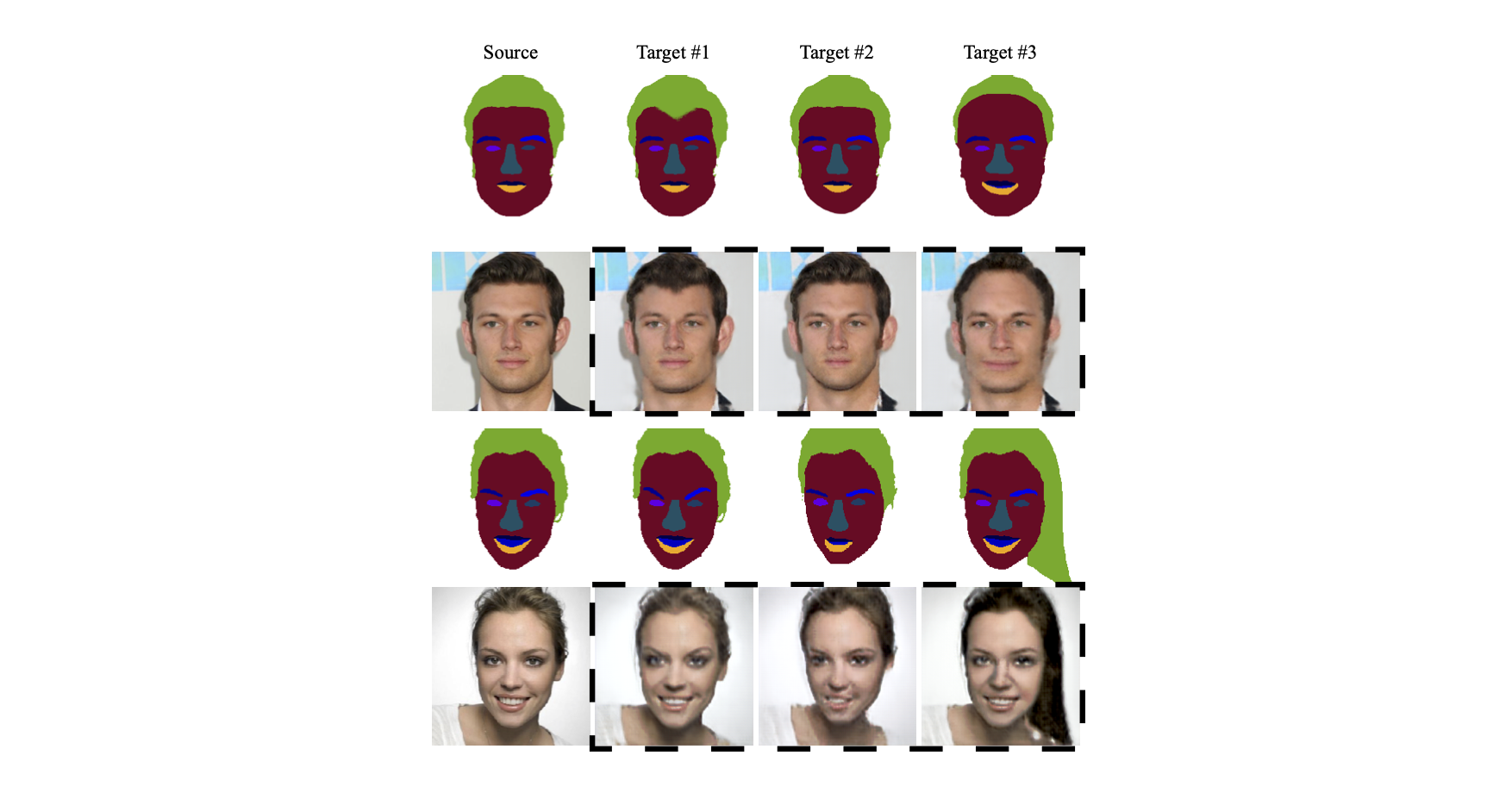
Face Editing
Acknowledegment
Thanks to Ke Sun, Yajing Liu for paper revision and labmates from the VIDAR group for helpful discussions.
bibtex
@inproceedings{SemIA,
author = {Jiacheng Li and
Zhiwei Xiong and
Dong Liu and
Xuejin Chen and
Zheng{-}Jun Zha},
title = {Semantic Image Analogy with a Conditional Single-Image {GAN}},
booktitle = {MM '20: The 28th {ACM} International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual
Event / Seattle, WA, USA, October 12-16, 2020},
pages = {637--645},
publisher = {ACM},
year = {2020},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3394171.3413601},
doi = {10.1145/3394171.3413601},
}